July 25, 2022
Reverse Osmosis, also known as RO (Reverse Osmosis), is a very advanced and effective energy-saving membrane separation technology that uses the pressure difference between the two sides of the membrane as the driving force to achieve membrane separation and filtration.
RO fundamentals and advantages
A reverse osmosis membrane is the core component to realize reverse osmosis technology, which is an artificial semi-permeable membrane with certain characteristics, made of polymeric material, simulating biological semi-permeable membrane material.
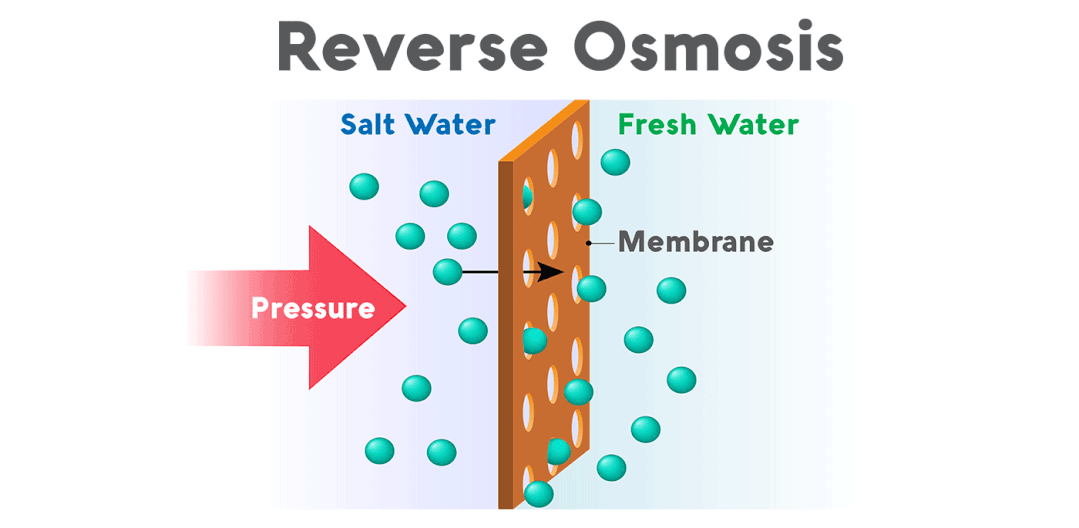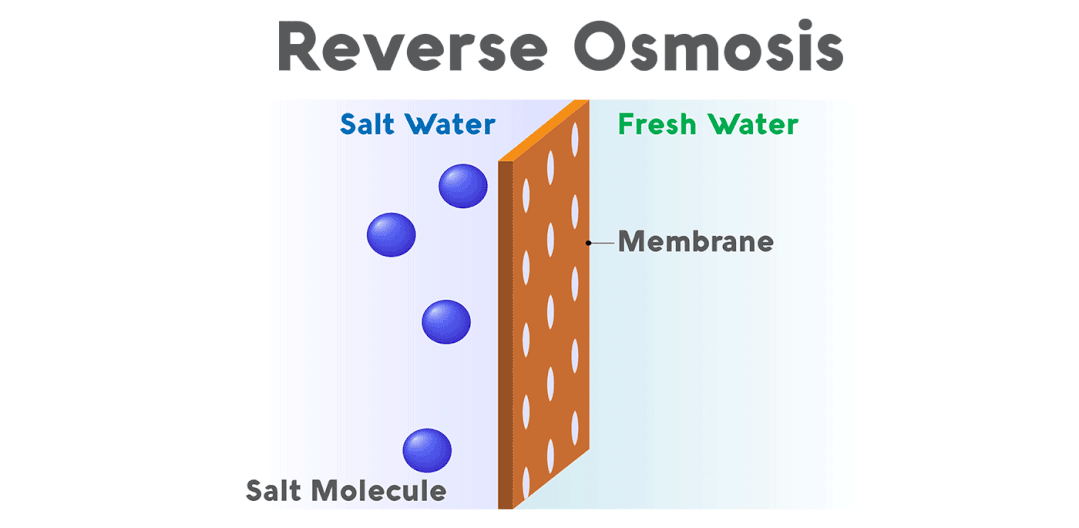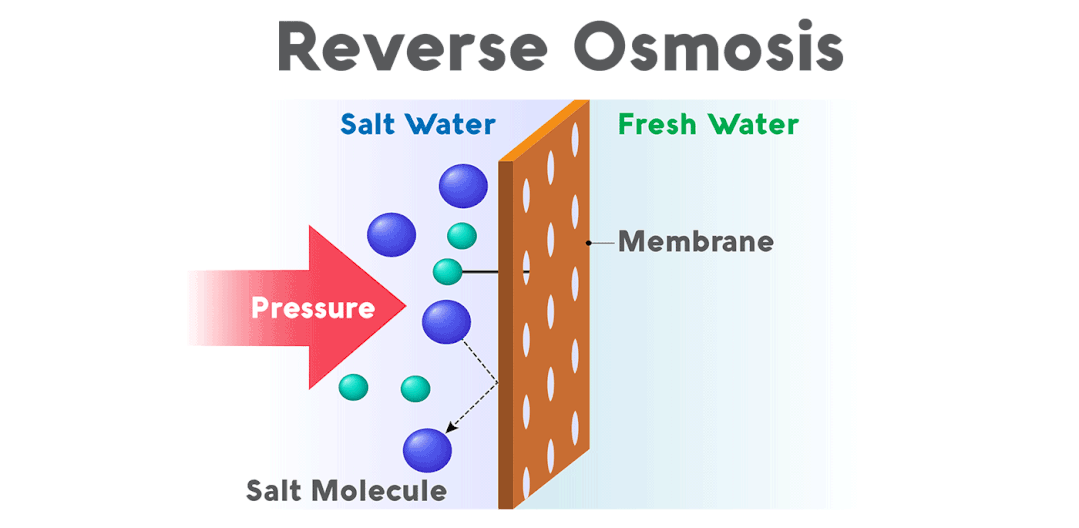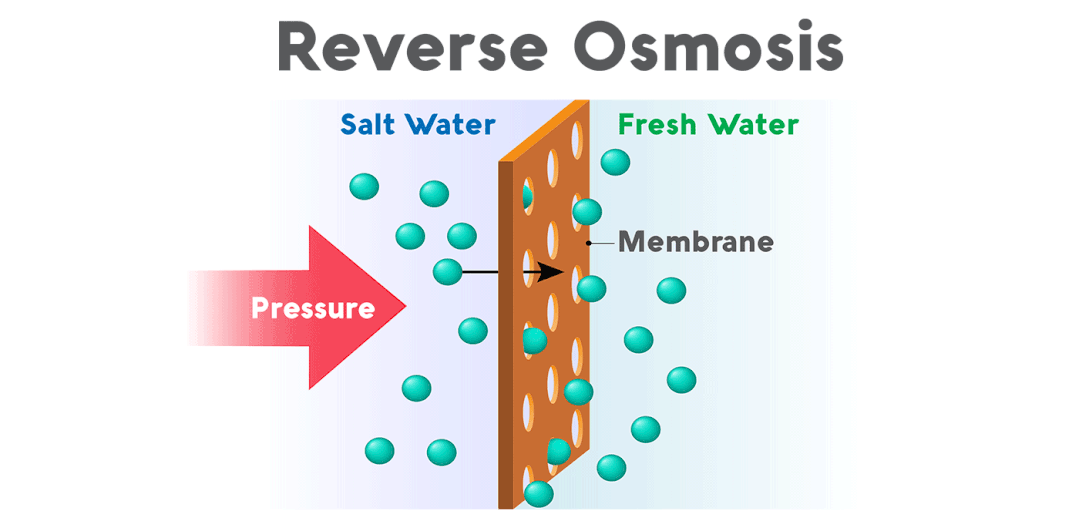
Reverse osmosis, also known as reverse osmosis, is a membrane separation operation that separates a solvent from an aqueous solution by using the pressure difference as the driving force and is the process of achieving water filtration of impurities. It is called reverse osmosis because it is in the opposite direction to natural osmosis.
The technical principle is to apply pressure to one side of the membrane under higher osmotic pressure than that of the solution, and when the pressure exceeds its osmotic pressure, the solvent permeates in the opposite direction, leaving these substances and water. The solvent obtained on the low-pressure side of the membrane is called the permeate; the concentrated solution obtained on the high-pressure side is called the concentrate.
If seawater is treated with reverse osmosis, fresh water is obtained on the low-pressure side of the membrane and brine on the high-pressure side. Then you can make reverse osmosis pressure to achieve the purpose of separation, extraction, purification, and concentration.
Reverse osmosis is a water treatment technology using membrane separation, which is a physical method of cross-flow filtration. Its advantages are as follows.
Lower operating costs at room temperature, relying on the pressure of the water as the driving force.
No large amount of waste acid and alkali discharge, not polluting the environment.
Simple system, easy operation, and a high degree of automation.
A wide range of adaptations to raw water quality and stable effluent water quality.
The small footprint of equipment, and small maintenance workload.
RO water treatment basic process
First, a stage one treatment process
After the liquid enters the membrane module, the pure water and concentration liquid is led out. Compared with other reverse osmosis water treatment process, the overall process is a more convenient, and simple operation, but has high limitations, and can not meet the higher water quality requirements.
The second is a multi-stage treatment process
On the basis of the one-stage treatment process, the liquid is concentrated in multiple steps. Compared with the one-stage treatment process, the process is more complex and can meet the higher water quality requirements and realize the recycling of water resources.
Third, is the two-stage one-stage treatment process
In the case of using a one-stage method is difficult to achieve the actual water quality requirements, you can use the two-stage one-stage treatment process. Compared with the above two primary processes, the use of two one-stage treatment processes can extend the application life of reverse osmosis membrane and does not require too much manpower to operate, and the corresponding treatment costs have been reduced.
Application of RO in water treatment:
Deep treatment of municipal wastewater
In the deep treatment of urban water pollution, reverse osmosis technology can lead to a higher recovery rate of wastewater and is more widely used.
Different materials of reverse osmosis membrane produce different water pollution deep treatment effects. Generally speaking, in urban water pollution deep treatment, after the treatment of urban residential sewage standards, the requirements for the treated water quality are higher (for example, water reuse), at this time, cellulose triacetate hollow fiber membrane, spiral coil polyvinyl alcohol composite membrane can play a better effect.
Compared with other RO membranes, both of them have a 100% retention rate of fecal coliform bacteria, no more than 1 degree of chromaticity, and 1mg/L~2mg/L permeate. At the same time, these two materials of reverse osmosis membrane have higher water flux and stronger anti-pollution ability.
Industrial wastewater treatment
1) Treatment of heavy metal ions
The application of reverse osmosis water treatment technology to industrial wastewater treatment is also very effective, in line with the general design principle of industrial economy and rationality, which can reduce energy consumption and operating costs as well as operational management difficulties.
Reverse osmosis units for industrial wastewater treatment are generally internal pressure tubular or coiled components with a stable pressure of about 218 MPa, which is excellent for heavy metal ion recovery. Among them, the operating pressure of the reverse osmosis plant based on internal pressure tubular components is stable at 217 MPa, where the recovery rate of nickel is above 99% and the separation rate of nickel is in the range of 97.12% to 97.17%.
2)Treatment of oily wastewater
Generally speaking, the oil in oily wastewater exists in three main forms, including emulsified oil, dispersed oil, and floating oil. In comparison, the treatment methods of dispersed oil and floating oil are relatively simple, relying on mechanical separation, precipitation, and activated carbon adsorption treatment, which can lead to a significant reduction of the corresponding oil content.
However, emulsified oil, it contains organic substances, can play the role of surfactants, and oil generally exists in micron-sized particles, so it has very high stability, it is difficult to effectively and quickly achieve water-oil separation.
With the support of reverse osmosis water treatment technology, it is possible to achieve concentration and separation without destroying the emulsion, followed by incineration of the concentration, recycling, or discharge of the permeate.
At present, in the treatment of oily wastewater, reverse osmosis water treatment technology is commonly used in combination with other treatment methods for the consideration of the final treatment effect and effluent quality.
For example, DEMUL-B1, a self-formulated emulsion breaker, was used to break the high concentration of O/W spinning oil wastewater, and then OSMONICS SE reverses osmosis membrane was used to further treat the broken water sample. The results showed that the COD removal rate of the water purified by the “emulsion-breaking-reverse osmosis” treatment reached 99.96%, and the oil content was almost undetectable.
Desalination of brackish water
In the process of desalination of brackish water, the introduction of reverse osmosis water treatment technology can effectively inhibit inorganic salt ions such as magnesium ions and calcium ions contained in brackish water, and realize the enhancement of pure water quality.
At this stage, people’s requirements for the quality of pure water, the original treatment method (adding scale inhibitor in brackish water) is difficult to meet people’s realistic requirements and the introduction of reverse osmosis water treatment technology for the inevitable choice.
In the operation of brackish water desalination using a reverse osmosis plant, it is necessary to regularly test the SDI index, strictly control the recovery rate, pay attention to the pressure difference between membrane modules, and measure the changes in water production and desalination rate in real-time. In practice, the desalination rate of the reverse osmosis plant is more than 96%, and the desalinated water quality meets China’s domestic drinking water standards.
How to deal with RO membrane contamination
Membrane contamination refers to the irreversible changes caused by the adsorption and deposition of particles, colloidal particles, or solute macromolecules in the liquid in contact with the membrane due to physical or chemical interaction with the membrane or the concentration of certain solutes on the membrane surface exceeding their solubility and mechanical effects on the membrane surface or the membrane pores, resulting in the reduction of membrane pore size or blockage, resulting in a significant decrease in membrane flux and separation characteristics.
Microbial contamination
1) Formation causes
Microbial contamination refers to the accumulation of microorganisms at the membrane-water interface, thus affecting the performance of the system.
These microorganisms use the reverse osmosis membrane as a carrier to reproduce and grow with the nutrient salts in the concentrated water section of reverse osmosis, forming a biofilm layer on the surface of the reverse osmosis membrane, resulting in a rapid increase in the pressure difference between the inlet and outlet water of the reverse osmosis system, a rapid decrease in water production and desalination rate, and contamination of product water.
Microbial biofilms can degrade membrane polymers or other reverse osmosis unit components directly (through enzyme action) or indirectly (through local pH or reduction potential action), resulting in shortened membrane life, and damage to membrane structural integrity, and even major system failure.
2) Control methods
Biological pollution can be controlled by continuous or intermittent disinfection of the incoming water. The raw water from the surface and shallow underground should be set up sterilization dosing device, chlorine type biocides, the amount of dosing generally to the residual chlorine content of the influent water > 1mg / L shall prevail.
Chemical contamination
1) Formation causes
The common chemical pollution is the deposition of carbonate scale inside the membrane element, in most cases, it is misoperation, imperfect scale inhibitor dosing system, interruption of scale inhibitor dosing in the operation process, etc.
If it is not found in time, the operation pressure will be increased, the pressure difference will be increased and the water production rate will be decreased within a few days, if the selected scale inhibitor does not match with the water quality or the dosing amount is not enough, the phenomenon of scaling inside the membrane element will also occur, the lighter scaling inside the membrane element can be restored through chemical cleaning, but in serious cases, it will also cause the scrapping of some membrane elements with serious pollution.
2)Control method
To prevent scaling in the membrane element, firstly, select the reverse osmosis scale inhibitor suitable for the water quality of the system, and determine the best dosing amount.
Secondly, strengthen the monitoring of the dosing system, pay close attention to the subtle changes in the operating parameters, and find the causes of abnormalities in time.
In addition, most of the reasons for high Fe3+ content in water are brought by the piping system, therefore, system piping including water source piping adopts steel-lined plastic piping as far as possible to reduce Fe3+ content.
Suspended particulate matter and colloid pollution
1) Causes of formation
Suspended particles and colloids are the main substances that foul the reverse osmosis membrane and are the main cause of SDI (sludge density index) exceeding the standard in the effluent.
The composition of suspended particles and colloids also varies greatly due to different water sources and regions. Usually, the main components of uncontaminated surface water and shallow groundwaters are bacteria, clay, colloidal silica, iron oxides, humic acid products, and artificially over-input flocculants coagulants (such as iron salts, aluminum salts, etc.) in the pretreatment system.
In addition, the formation of precipitation by the combination of positively charged polymers in raw water and negatively charged scale inhibitors in the reverse osmosis system is also one of the causes of such pollution.
2)Control method
When the content of suspended matter in raw water is >70mg/L, the pretreatment method of coagulation, clarification and filtration are usually used; when the content of suspended matter in raw water is <70mg/L, the pretreatment method of coagulation and filtration is usually used; when the content of suspended matter in raw water is <10mg/L, the pretreatment method of direct filtration is usually used.
In addition, microfiltration or ultrafiltration is a recently emerged effective way of membrane treatment of turbidity and non-dissolved organic matter, which can remove all suspended matter, bacteria, most colloids, and non-dissolved organic matter, and is a more ideal pretreatment process for reverse osmosis system.
Precautions for RO application
In reverse osmosis technology in the process of water treatment applications, the necessary filtration of sewage should be carried out. Filtration is the basis for RO technology to function, and the filtration process should be strictly controlled to avoid impurities from entering the RO system mixed with water to protect the permeate membrane and equipment, improve the water output and reduce the possibility of corrosion.
The reverse osmosis device should be flushed regularly, especially for scale cleaning, to maintain the good performance of the semi-permeable membrane and extend the service life of the device.
When not in use, the reverse osmosis unit is affected by the accumulation of sewage, which can breed microorganisms. Therefore, it needs to be flushed and disinfected during the downtime of the unit, and the temperature during the downtime should be well set to protect the reverse osmosis membrane.
Operators should strictly abide by the operating procedures and operating specifications, continuously improve their professional quality, and carefully check the device before use to avoid damage to the device due to operator errors, so as to ensure that the device can operate normally and carry out wastewater treatment work smoothly.
Detailed Operating Instructions for Automatic Dosing Systems
December 26, 2024
Characteristics and Applications of Precision Filters
December 19, 2024



